Electronic energy meters are very important for power enterprises to measure electrical consumption.
It can directly influence economic benefits of power companies and interests of users that the meters operate in a correct and reliable way.
So testing every single meter is very crucial.
Meter testing equipment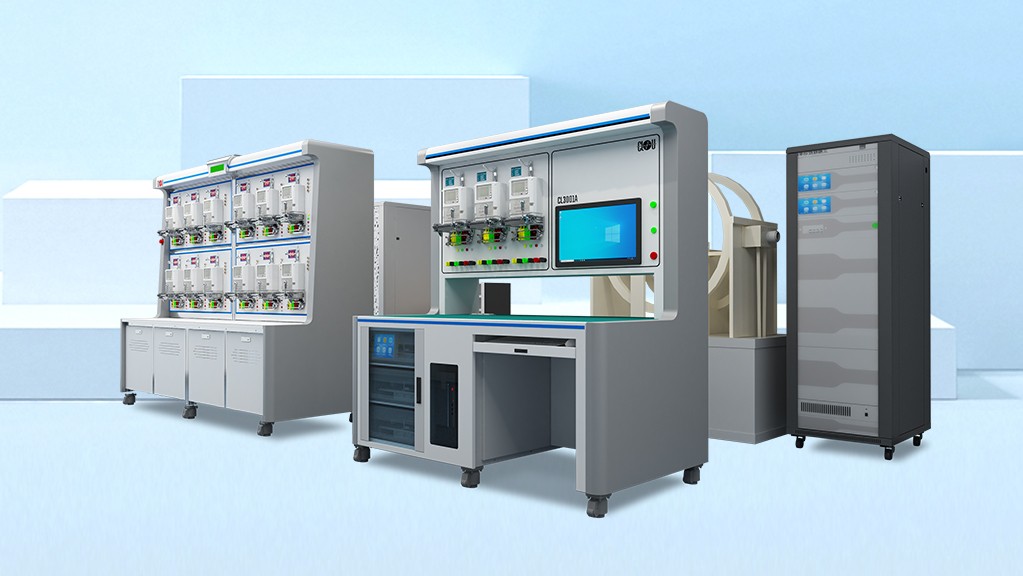 Introducing Our High-Quality Meter Test Equipment for Precise Measurements mainly includes meter verification device, whose performance can ensure meter testing results.
Introducing Our High-Quality Meter Test Equipment for Precise Measurements mainly includes meter verification device, whose performance can ensure meter testing results.
In this article, we will introduce CLOU precision meter testing devices while explaining the whole life of energy meters.
Meter Life
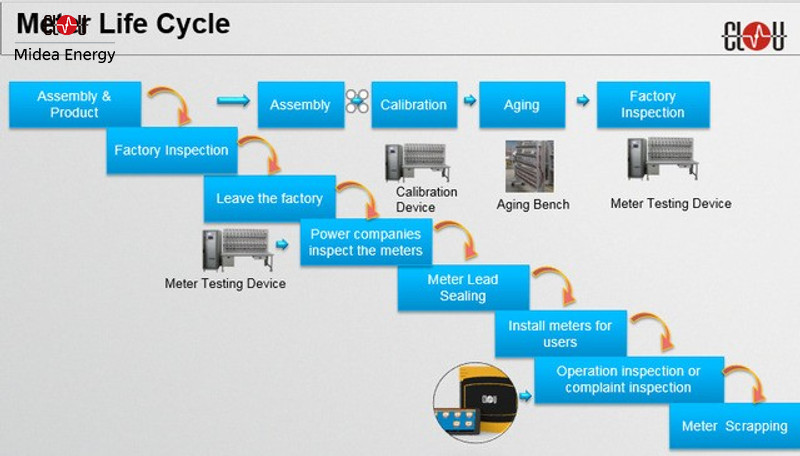
Production Cycle
Energy meters must go through these four processes before sending out from meter manufacturers: assembly -> calibration -> ageing -> factory inspection.
Meter manufacturers first finish assembling meters after receiving orders, then adjust and calibrate The difference between adjustment and calibration the metering accuracy of meters.
The difference between adjustment and calibration the metering accuracy of meters.
In this process, we use our high-precision reference instruments with calibration function (standard meters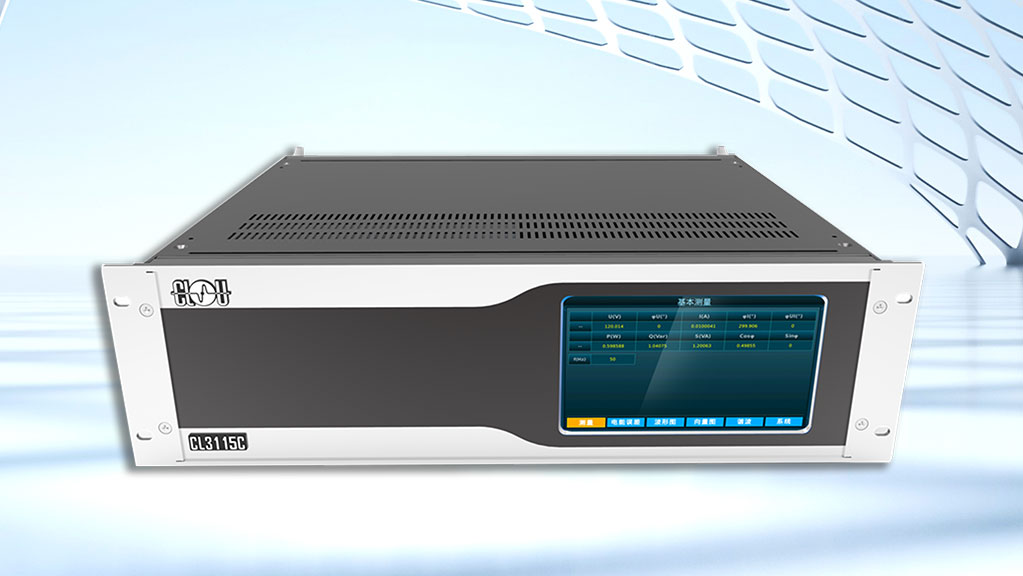 Class 0.05 Three Phase Multifunctional Standard CL3115C) to calibrate.
Class 0.05 Three Phase Multifunctional Standard CL3115C) to calibrate.

The next step is ageing. Ageing meter process means, under the condition that all meter functions are normal after calibration, power the meters on for a long time to check their functions like metering and communication are normal.
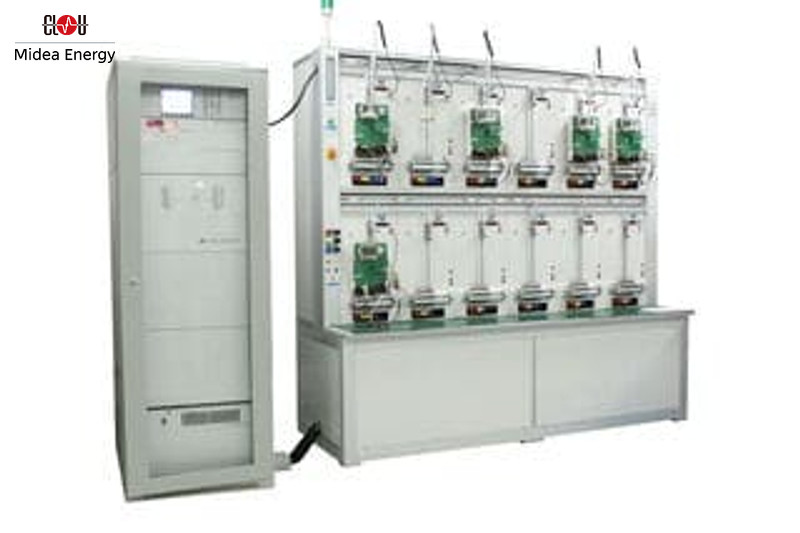
 Rail-Mounted Electric Energy Meter Testing Device CL3000
Rail-Mounted Electric Energy Meter Testing Device CL3000Finally, manufacturers need to test the meters in details and in all respects in order to verify if they meet all the requirements  Acceptance tests for energy metersof products.
Acceptance tests for energy metersof products.
This process applies to the meter testing bench.
Service Life Cycle
From leaving the manufacturer factories to power companies, the service life cycle of meters is as follows:
arrival inspection of power companies -> meter sealing -> install meters for users -> operation inspection or complaint inspection -> dismantle test -> meter scrapping.
After being delivered from the meter factories, the meters shall be centrally inspected in the metering centre of the power grid company to test the metering function and performance on sample base. Typically, it's 4% of the supplied volume. Country regulations apply, so e.g. Germany requires a 20% sampling.
This link can be completed by using the meter testing devices or automatic verification assembly line.
Then, the face-covers of the meters are sealed Sealing of Energy Meters to avoid a manipulation of the metering results.
Sealing of Energy Meters to avoid a manipulation of the metering results.
The meters are stored in the warehouse to use after this step.
When users of the power companies have metering demand, take meters out from the warehouse and install it on site.
After installation, operations staff will be arranged to test the meters on site if the meters can continue to use, whenever they receive customers'complaint or find any abnormal on site.
The meters will be re-tested for accuracy and performance after a certain number of years, depending on the country metrological institute. A typical period is 8 years after installation. If the inspection is PASS, the meters can remain in the field for another 4 years. All following periods for re-check are 4 years.
The given meter-lifetime is conservatively calculated on component base and with the help of accelerated life tests Accelerated Life Test for Energy Meters.
Accelerated Life Test for Energy Meters.
Conclusion
The meter testing device is a measurement standard instrument used to verify the energy meters, which is to ensure the accuracy and traceability of the electric energy measurement values.
The meter testing devices described above are all developed and manufactured by our CLOU company. We have over two decades of meter manufacturing experience.
If you are looking for information about meter testing, contact us Contact Us or leave your comment.
Contact Us or leave your comment.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in January 2022 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.






The ageing cycle not include more test than power the meter for a long time? I suppose that other test shall be necessary, like a climatic test.
Thanks for your comment, Jorge. In the article described is the routine procedure during production. The meters come during this process for 24 hours in a climatic chamber with 60°C and are powered up with nominal load. You could also call it 'burn in'. Not many meter manufacturers are doing this, as it increases the production cost. What you mean is the accelerated life test, which takes several months. This test is done on sample base only.
From your explanation I understand the lifespan of an electronic meter is approximately 12 years. Am I right?
Explained in the article is the strategy for power companies in European countries. Eight years after installation, you make a laboratory- or onsite test on sample base for the installed batch. Then you repeat the test for the same batch after another four years. It indicates only the inspection intervals. Means:
8 years -> 4 years -> 4 years -> 4 years and so on. There is no general rule for these inspections. I saw in Middle East 5 years intervals after installation. Some companies never re-test. I prefer the European strategy. The proper functionality for electronic meters can be seen now in the field (e.g. Italy starting in year 2001). They now gradually change the meters. Regular performance monitoring helps for utility evaluation and budget planning.