Sometimes it happens that you touch the door knob and you get an electrical shock. It's not dramatically for your body but an unpleasant feeling.
What happened?
Your body was electrostatic charged by friction between your wool pullover and synthetic fabrics. Or your shoes are insulating you nice while walking on a carpet. Low humidity is supporting the charging of your body.
If you want to feel the electrical discharge more intense, you touch something direct connected to earth-potential, like the water tap.

This sort of electrical shock is called electrostatic discharge (ESD) and it can damage electronic components.
Electronic energy meters need to be resistant versus this discharge.
Beside the meter functionality it's also important that the registers are not changing higher than the allowed critical change value.
The Electrostatic discharge immunity test
The applicable standard for our energy meter testing is the IEC/EN 61000-4-2 together with the requirements given in IEC 62052-11 Ed2.
It states for the number of discharges: 10 discharges at each test point and in the most sensitive polarity. If sensitivity is not known then 10 discharges shall be applied in both polarities with at least 1 s between discharges.
What is a test point?
See my interpretation together with the tests below.
Do we know the most sensitive polarity?
The type test engineers don't care, so the test is done with 10 discharges in both polarities.
Why do we need to wait at least one second?
Maybe you saw some film where people are reanimated with a defibrillator. This device needs a certain charging time for the internal capacitor. For our ESD gun the same thing applies. Modern ESD guns will not release the discharge when the required voltage isn't reached, older ones release the discharge when you pull the trigger.
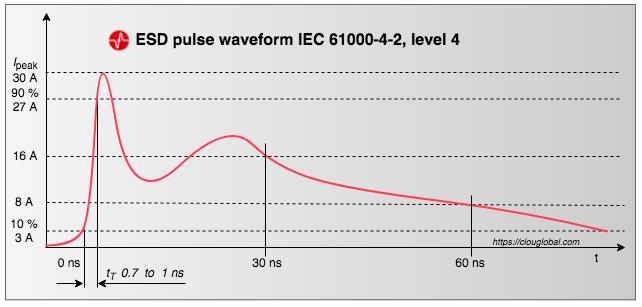
ESD is a high-current event. Energy meters are tested acc. to IEC level 4. The first peak current is 30 A, after 30 ns we have 16 A and after 60 ns we have 8 A. If the charging time is too short, we have a spark but not the current.
Wait one second and the test results will be repeatable and comparable.


We have per IEC62052-11 three different tests. The PASS/FAIL evaluation has to be done for each test individually. Means, you read the SUM registers for active- and reactive energy before and after the test. The value change must be below the critical change value. During the test the highest specified nominal voltages are applied to the meter. A three-phase meter needs of course a three-phase power supply. The current terminals remain open.
Indirect Discharge
Simplified:
You touch the kitchen sink. It's for the water tap and surrounding parts an indirect discharge. For you it's only less intense.
In IEC wording:
The test voltage of 8 kV shall be applied to both vertical and horizontal coupling planes in contact mode. In both vertical and horizontal plane, all faces of meter shall be exposed to the discharge.
We are using the tip for contact-discharge.
The test points
If the meter has a cuboid shape, it has 6 surfaces. Except of ANSI meters all energy meters have this shape.
So, we have 6 surfaces, 2 polarities, 2 coupling planes and 10 discharges each, makes in total 240 discharges to finish this test. Keep the 10 cm distance to the coupling plates in mind.
Contact Discharge
Simplified:
You touch the water tap and receive the full electrical discharge shock.
In IEC wording:
The test voltage of 8 kV shall be applied to metallic parts accessible in normal operation.
Normal operation for an energy meter is completely closed, including terminal cover.
Which metallic parts do we have?
We have the sealing screws for the terminal- and face cover, eventually also sealing screws for the battery slot and for communication modules. Some meters have still metallic hooking plates. These are the elements which we have to test with contact discharge.
We are using the tip for contact-discharge.
The test points
10 discharges for each metallic part in both polarities
Air Discharge
Simplified:
Your fingers are very close to the water tap and your body is already discharged.
In IEC wording:
The test voltage of 15 kV shall be applied to non-metallic parts accessible in normal operation.
We are using the tip for air-discharge.
The test points
We have 6 surfaces, 2 polarities and 10 discharges, makes 120 discharges. You can do this test on any point of the surface. Typically, you distribute the discharges regularly on the surface.
Thank you for reading. If you have another interpretation for the test-points, let's discuss.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.





All comments are moderated before being published. Inappropriate or off-topic comments may not be approved.