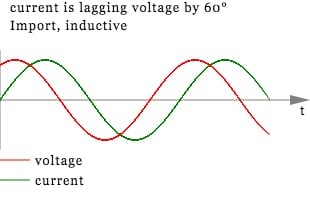
All electronic energy meters have a crystal oszillator. It's essetial for sampling and for determination of the zero-crossings. When we know the time difference between zero-crossing of voltage and current, we can calculate the phase shift.
In the four-quadrant simulation you can adapt different phase angles to get a better idea about the phase shift.
Finally the phase shift is expressed as power factor.
For CLOU meters the chip-internal oscillator frequency is with 12.288 MHz about 5 times higher than needed for energy meters class 0.2.
For a real time clock (RTC) CLOU energy meters are operating with an external quartz crystal with a frequency of 32.768 kHz. Together with electronic compensation for accuracy and temperature change, we are better than the by IEC 62054-21 required values for time switches.
What are the tasks for a Real Time Clock?
The RTC is responsible for:
- keeping the internal calendar,
including year, month, day, day of the week, hour, minute, second, leap year, daylight-saving - controlling of the tariff structure
- demand measurement
- billing reset at the end of the month
- DST (daylight-saving time) switchover
- time stamps for events (e.g. tamper, outage …)
Together with an AMI system, even more functions can be enabled. You can include special days or periods for special tariff rates. Christmas works without AMI, but think about Lunar New Year or the End of Ramadan. Typically, an energy meter with calendar function is holding two calendars. It's the active calendar for the actual year, and a passive calendar for the next year.
Means, without AMI system you have one year time to walk around and update all your 5 million meters in the field with the new passive calendar.
I don't know any utility doing this. Nevertheless, it's also possible.
In addition, an AMI-system can synchronize the time for all meters. According to IEC 62054-21 the meter RTC has an allowed tolerance of max. +0,5 s/24 h under reference conditions. At 45 °C it's already ±3,3 s/24 h. So, a regular synchronization is reasonable for high-end energy meters.
In case of power-outage, the meter takes the required RTC power-supply first from the internal super-capacitor. If the outage is longer, the RTC is backed by a battery.
Now, for fun let's make a time comparison. If you don't see the clocks, your browser has the javascript-function disabled.
Here you can compare your PC/Mobile time with our server time. If the second indications are not equal, either your computer time is not synchronized or our server. Since we do a permanent synchronization on each request, I personally would exclude the server.
Thank you for reading. If you have real time, just drop me a comment.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in July 2021 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.





Quite informative.
Patricia, thanks for taking a look and kind comment.