The transition to renewable energy makes it harder than ever to provide energy reliably where and when it is required, considering the enormous quantity of energy consumed in today's modern world and government goals to reduce carbon emissions. As a result, there is a growing need for energy storage devices. The power conversion system (PCS) is a crucial element of any effective energy storage system (ESS). Between the DC batteries and the electrical grid, the PCS serves as an interface.
How does a PCS work?
To achieve the bidirectional conversion of electric energy, a power conversion system is a component connected between the energy storage battery system and the power grid. The PCS charges the batteries in the event of excessive power generation. The PCS provides the power with the stored energy if the grid need extra energy.
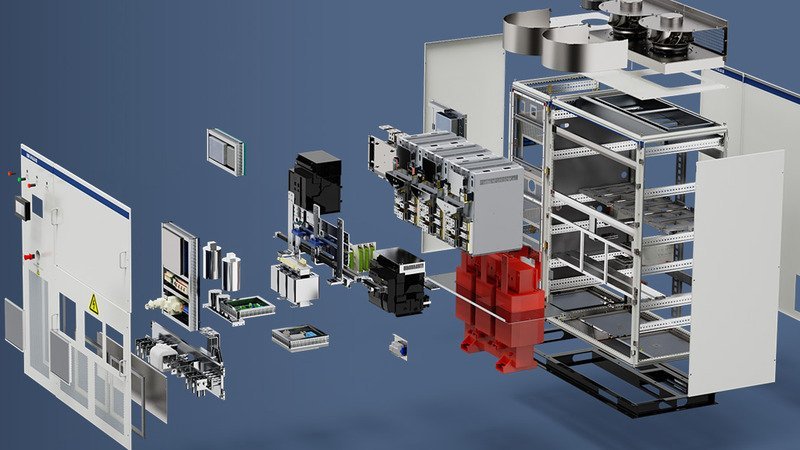
AC/DC bidirectional converters, control elements, switching components, and cooling compose a power conversion system. There are many layers of remote control for the system. This is designed to regulate the battery's charge or discharge, as well as the grid's active and reactive power. In order to obtain information about the state of the battery pack and cells, the PCS can simultaneously connect with the battery management system (BMS) using a number of interfaces and protocols (RS-485, CAN, Fibre-Optics, Ethernet). As a result, the battery can be charged and discharged safely, and the energy storage system can run without interruption.
How is a PCS integrated in an energy storage system?
The block drawing has been streamlined. Renewable energy embedded systems may become exceedingly complex. We can construct entire systems or standalone devices thanks to our modular designs and wide range of ratings.
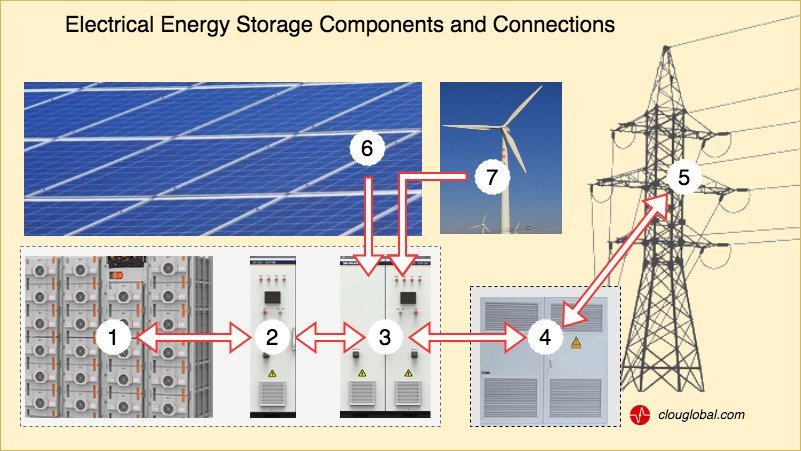
| No. | Item |
|---|---|
| 1 | Battery racks, consisting of cell modules, e.g. Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) modules (64 V) for charging and discharging at high speed, or lithium with nickel, cobalt and manganese as cathode (NCM) which allows a higher density and lower temperatures (52 V). |
| 2 | Battery management system (BMS), either as a part of the battery clusters or as central control device |
| 3 | Power conversion system (PCS) The devices can be either integrated in a storage container or with separate housing for outdoor use. |
| 4 | Transformer station to adapt to the grid |
| 5 | Power grid |
| 6 | Solar power plants provide DC, which needs to be converted to the required DC voltage level. |
| 7 | Wind turbines are connected to the PCS on the DC side (voltage must match, see #6) or, if already inverted, on the AC side. |
Where are the suitable points for energy metering?
We recommend having bidirectional energy meters on DC-side and AC-side of the power conversion system. This gives an indication for the conversion losses.
For billing purpose, a bidirectional CT/PT meter is installed at the transformer station.
Additional meters at the PCS can be for generated solar- and wind power.
Our PCS Certifications (selection)
Our devices are tested and approved by various organizations
- GB/T 12325
Power Quality Supply Voltage Deviation - GB/T 14549
Power Quality Harmonics of Public Grid - GB/T 15543
Power Quality Three-phase Voltage Unbalance - GB/T 15945
Power Quality Power System Frequency Deviation - UL 1741
UL Standard for Safety Inverters, Converters, Controllers and Interconnection System Equipment for Use With Distributed Energy Resources - UL 1741 SA
SA is short for Supplement A, an addition to the existing UL 1741 standard designed to create a standard for inverters more capable of dealing with a volatile grid and future-proofing by creating a standard for inverters to actively manage grid functions. Products which meet these requirements are known as Grid Support Inverters, Smart Inverters or Advanced Inverters. - IEEE 1547
IEEE Standard for Interconnection and Interoperability of Distributed Energy Resources with Associated Electric Power Systems Interfaces
Takeaway
A power conversion system is a mono- or bidirectional converter that can control the charging and discharging of batteries, perform AC and DC conversions, and directly supply power to an AC load in the absence of a power grid. Talk to us, our experts will be pleased to provide the right configuration for your application.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in November 2022 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.





A PCS is a bidirectional converter, meaning it can both convert AC (Alternating Current) from the grid to DC (Direct Current) for charging batteries, and convert DC from batteries back to AC to supply power to the grid or a load.
Thank you for your comment. You're absolutely correct in emphasizing the bidirectional capability of most Power Conversion Systems (PCS), which allows for the conversion of AC to DC and vice versa. This is especially pertinent in systems designed for energy storage and integration with the grid. I appreciate you pointing this out, as it clarifies the typical functionality expected from a PCS in today's energy landscape. It's worth noting that some PCS configurations may still operate in a unidirectional manner, catering to specific applications that do not require bidirectional flow. Your input is invaluable, and it's great to have contributions from knowledgeable readers like yourself who help enhance the accuracy and completeness of the information we share. Thank you once again for enriching the conversation.